
10 Business Process Automation Examples to Boost Efficiency
Discover 10 real-world business process automation examples. Learn how to streamline workflows in finance, HR, and sales to save time and reduce costs.
Business process automation is more than just a buzzword; it's a fundamental shift in how modern teams operate. It involves using technology to execute recurring tasks or processes in a business where manual effort can be replaced. The goal isn't to eliminate human involvement but to free up your team's time for high-value work that requires critical thinking, creativity, and strategic planning. By automating the predictable, you empower your people to focus on the exceptional. To grasp the foundational concepts of redefining workflows, it's beneficial to understand the definition and scope of workflow automation.
This article moves beyond theory to provide concrete business process automation examples that you can implement immediately. We will dissect 10 common workflows, from invoice processing to customer onboarding, and break down exactly how to automate them. For each example, we'll offer a strategic analysis, tactical insights, and actionable steps you can replicate. You will see how tools like Tooling Studio’s extensions for Gmail and Google Tasks can centralize these automated processes directly within your existing Google Workspace, creating a unified and efficient operational hub. Get ready to transform your team's productivity by turning routine tasks into streamlined, automated systems.
1. Invoice Processing Automation
Automated invoice processing is a prime example of business process automation that delivers tangible ROI by streamlining accounts payable. This technology uses optical character recognition (OCR) and machine learning to automatically capture, validate, and process vendor invoices, eliminating tedious manual data entry. The system extracts key information like vendor name, invoice number, and line-item details.
This data is then automatically cross-referenced against purchase orders and delivery receipts in a process known as three-way matching. Invoices that match are routed for payment, while exceptions are flagged for human review. This drastically reduces processing time and errors. For example, Ford Motor Company processes over 5 million invoices annually with 99% accuracy using automation.
Strategic Breakdown
- High-Volume, Low-Complexity: Automating invoice processing is most effective for businesses handling a large volume of standardized invoices. The repetitive nature of this task makes it a perfect candidate for automation, freeing up AP teams for more strategic work like vendor relationship management and cash flow analysis.
- Accuracy and Compliance: Automation enforces business rules consistently, ensuring every invoice undergoes the same validation and approval process. This improves accuracy, reduces the risk of fraudulent payments, and creates a clear, auditable trail for compliance purposes.
The following diagram illustrates the core automated workflow, from initial data capture to final approval.
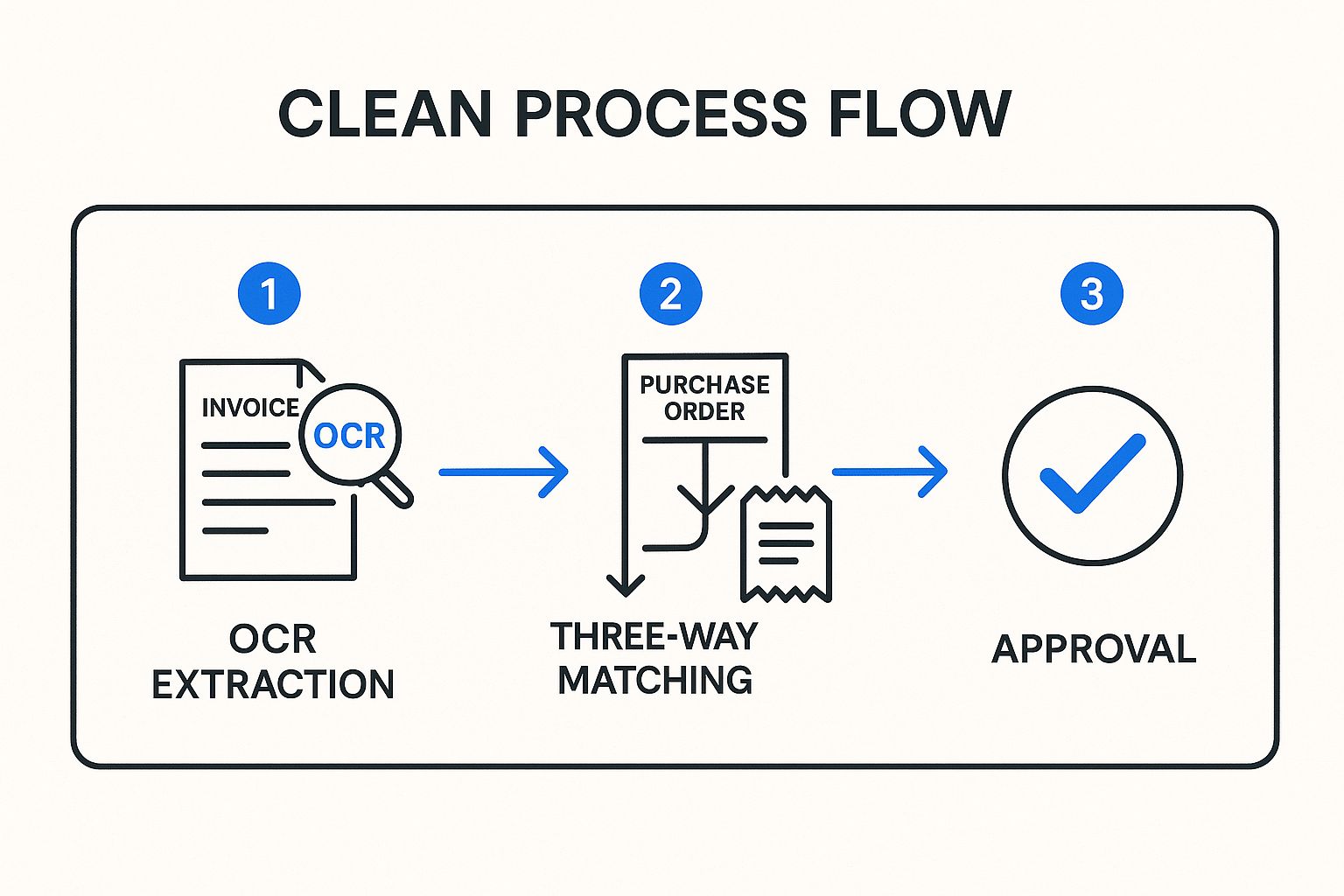
This streamlined process visualizes how automation connects disparate documents to validate transactions before they reach the final approval stage, ensuring accuracy and speed.
2. Customer Onboarding Automation
Automated customer onboarding is another powerful business process automation example that significantly impacts customer satisfaction and retention. It streamlines the initial journey for new clients, automating everything from welcome emails and account setup to compliance checks and initial training. This process uses triggers and conditional logic to guide customers through necessary steps, ensuring a smooth and consistent welcome experience.
This automation eliminates manual handoffs between sales, support, and success teams, reducing the risk of dropping the ball. For instance, fintech company Revolut onboards new customers in minutes using automated identity verification, a process that once required significant manual effort. Similarly, HSBC's digital onboarding initiative boosted completion rates by 85% by creating a frictionless, automated path for new clients.
Strategic Breakdown
- First Impression and Retention: The onboarding phase is a critical touchpoint that sets the tone for the entire customer relationship. Automation ensures every customer receives a timely, professional, and helpful welcome, which directly correlates with long-term retention and reduces early-stage churn.
- Scalability and Consistency: As a business grows, manually onboarding each new customer becomes unsustainable. Automation allows you to scale your onboarding process infinitely without sacrificing quality. It enforces a standardized workflow, guaranteeing every customer completes key activation steps and receives the same high-quality introduction to your product or service.
The diagram above illustrates how automation can connect initial sign-up actions to a series of guided steps, personalized communication, and necessary verifications. This creates a cohesive journey that activates customers efficiently and sets them up for long-term success.
3. Employee Payroll Processing
Automated payroll is a critical business process automation example that minimizes risk and ensures employee satisfaction. This technology orchestrates the entire payroll cycle, from collecting time and attendance data to calculating gross pay, deducting taxes and benefits, and disbursing net pay. It integrates with HR information systems (HRIS) and time-tracking tools to create a seamless, accurate flow of data.
The system automatically applies correct tax rates and withholding rules, drastically reducing the chance of costly compliance errors. For instance, global companies like General Electric have leveraged automation to reduce payroll processing costs by up to 30%, ensuring consistency across diverse operational units. Similarly, large-scale employers like Walmart rely on these systems to manage complex payroll for millions of employees with precision.
Strategic Breakdown
- Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Payroll is governed by strict, ever-changing federal, state, and local regulations. Automation is the most reliable way to enforce these rules consistently, calculating withholdings and generating tax forms accurately. This creates an essential, auditable record that protects the business from penalties and legal challenges.
- Scalability and Complexity: Automated systems are designed to handle complexity, from variable hourly rates and overtime to commissions and bonuses. As a business grows, the system scales effortlessly, managing an increasing number of employees and diverse compensation structures without a proportional increase in administrative overhead, making it a cornerstone of sustainable growth.
4. Order Fulfillment and Inventory Management
Order fulfillment automation is a powerful business process automation example that integrates order processing, warehouse operations, and shipping into a cohesive system. This technology automatically processes incoming customer orders, checks inventory levels in real-time, generates pick lists for warehouse staff, updates stock counts, and selects the optimal shipping carrier. It also provides customers with automated tracking information, enhancing the post-purchase experience.
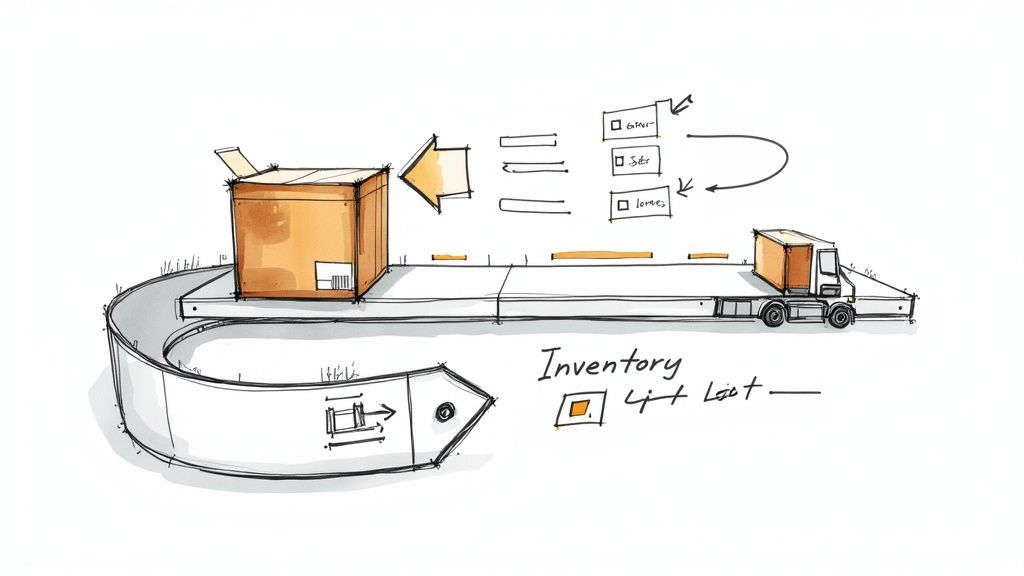
This automated flow, from order placement to final delivery, minimizes human error and significantly accelerates the entire fulfillment cycle. For instance, Amazon's world-class fulfillment centers leverage this automation to process millions of orders daily with 99.99% accuracy, while Zara uses an automated inventory system to power its fast-fashion supply chain.
Strategic Breakdown
- Scalability and Speed: Automating fulfillment is crucial for businesses experiencing growth. It allows them to handle increasing order volumes without a proportional increase in manual labor, ensuring that speed and accuracy are maintained as the company scales. This is a key component of effective workflow automation for small businesses.
- Inventory Accuracy and Cost Control: Automation provides a real-time, accurate view of inventory. By implementing barcode or RFID tracking and establishing safety stock levels based on demand, businesses can prevent stockouts and overstocking. This precision reduces carrying costs and lost sales, directly impacting the bottom line.
The video below demonstrates how warehouse automation systems streamline the picking, packing, and shipping processes.
This level of operational visibility and control shows how automation transforms a traditionally labor-intensive function into a strategic asset for customer satisfaction and profitability.
5. Lead Generation and Qualification
Automating lead generation and qualification is another impactful business process automation example that directly fuels revenue growth. This system works across multiple channels to attract, capture, and qualify potential customers. It automatically scores leads based on their demographic data and online behaviors, like website visits or email opens, nurtures them with personalized content, and routes only the most sales-ready leads to the team.
This process integrates website forms, social media, and CRM systems into a cohesive lead management engine. For instance, HubSpot generates over 100,000 leads monthly through its automated marketing platform. Similarly, Salesforce customers have seen lead conversion rates increase by up to 45% by implementing automated lead scoring, ensuring sales reps focus their energy on the most promising opportunities. This automation transforms a manual, often disjointed process into a streamlined, data-driven pipeline.
Strategic Breakdown
- Sales and Marketing Alignment: Automation is most powerful when it bridges the gap between marketing and sales. By co-creating clear lead scoring criteria, both teams agree on what defines a qualified lead. This ensures marketing delivers high-quality prospects and sales follows up effectively, eliminating friction and maximizing conversion rates.
- Scalable Personalization: Lead nurturing automation allows businesses to deliver personalized experiences at scale. By mapping content to different stages of the buyer journey and using triggers based on user behavior, you can send the right message at the right time. This builds trust and guides prospects toward a purchase decision without manual intervention for every interaction.
6. IT Help Desk and Ticket Routing
Automating the IT help desk is a powerful business process automation example that streamlines how support requests are managed. This technology uses natural language processing (NLP) to understand, categorize, and prioritize incoming tickets. It automatically routes issues to the right technicians based on their skills and current workload, drastically reducing manual triage and response times.
This automation provides self-service options for common, well-documented problems, empowering users to find solutions instantly. For example, IBM's Watson-powered help desk resolves an estimated 60% of tickets without human intervention, while ServiceNow customers often report a 25% improvement in first-call resolution rates. This ensures service level agreements (SLAs) are met consistently and frees up IT staff for complex, high-impact tasks.
Strategic Breakdown
- Tiered Automation Strategy: The most effective approach is to start by automating Tier 1 support for common, high-volume issues like password resets or software access requests. This creates an immediate impact by deflecting a significant portion of tickets, allowing human agents to focus on more complex Tier 2 and Tier 3 problems.
- Knowledge-Driven Improvement: An automated help desk relies on a robust and consistently updated knowledge base. Analyzing ticket patterns reveals gaps in documentation and opportunities for new self-service solutions. This creates a feedback loop where the system becomes smarter and more efficient over time, continuously improving resolution rates.
For IT professionals looking to implement similar streamlined workflows, you can learn more about how an IT support specialist can use a Kanban board in Google Workspace.
7. Expense Report Processing
Automating expense report processing is a powerful business process automation example that revolutionizes how companies manage employee expenditures. This technology eliminates cumbersome manual paperwork by using mobile apps for receipt capture, optical character recognition (OCR) for data extraction, and rule-based workflows for policy validation and approvals. Employees simply snap a photo of a receipt, and the system automatically populates the expense report.
The data is then validated against company policies, checking for spending limits and approved categories. Compliant reports are routed directly for managerial approval and then to finance for reimbursement, often integrating with accounting software. For instance, PwC achieved 90% straight-through processing for expense reports, and American Express cut its processing costs by 65% through automation, showcasing significant efficiency gains.
Strategic Breakdown
- Policy Enforcement and Control: Automation enforces expense policies consistently across the organization. By setting predefined rules for spending limits, required documentation, and approval hierarchies, it minimizes non-compliant spending and reduces the risk of fraud. This ensures fairness and transparent financial governance.
- Employee Experience and Productivity: Tedious expense reports are a common pain point for employees. Automating the process with mobile-first tools not only saves them time but also accelerates reimbursement cycles. This improves employee satisfaction and allows them to focus on their core responsibilities rather than administrative tasks.
8. Email Marketing Campaigns
Email marketing automation stands as a powerful business process automation example, allowing companies to deliver personalized, triggered email sequences based on customer behavior. This process involves segmenting audiences, personalizing content, and scheduling sends to engage subscribers at precisely the right moment. The system tracks metrics and adjusts campaigns automatically to maximize open rates, click-throughs, and conversions.
This automation transforms generic email blasts into dynamic, one-to-one conversations. For instance, Netflix leverages automated emails to re-engage dormant users, contributing to a significant reduction in customer churn. Similarly, Spotify’s automated emails about personalized playlists help boost user engagement, keeping subscribers active on the platform. These automated workflows turn customer data into timely, relevant communication.
Strategic Breakdown
- Behavior-Driven Personalization: The core strength of this automation is its ability to react to user actions. A customer abandoning a shopping cart, viewing a specific product, or reaching a milestone can trigger a tailored email sequence. This behavioral targeting makes messages highly relevant, increasing the likelihood of conversion and fostering customer loyalty.
- Scalable Engagement and Nurturing: Automation allows businesses to nurture leads and engage customers at scale without a proportional increase in manual effort. It ensures no lead is forgotten and every customer receives timely follow-ups, from welcome series to re-engagement campaigns. This creates a consistent brand experience and systematically moves customers through the sales funnel.
9. Document Approval Workflows
Document approval automation is a critical business process automation example that streamlines the entire lifecycle of reviewing and signing off on key business documents. This technology creates a structured digital path for contracts, proposals, and internal policies, routing them to the correct stakeholders in a predefined sequence. It manages version control, sends automated reminders for pending actions, and captures electronic signatures, replacing chaotic email threads and manual follow-ups.
This system provides a centralized, transparent view of where every document stands in the approval process. For instance, platforms like DocuSign and Adobe Sign have transformed contract management, reducing approval cycles from weeks to mere hours by digitizing the entire workflow. This not only accelerates business operations but also significantly improves compliance and record-keeping.
Strategic Breakdown
- Risk Mitigation and Version Control: Automation eliminates the risk of stakeholders approving outdated document versions. The system locks a document once the approval process begins and ensures everyone is working from a single source of truth. This is vital for legal contracts, financial reports, and regulatory filings where precision is non-negotiable.
- Visibility and Accountability: Automated workflows provide complete transparency, tracking every action from submission to final approval. This creates a clear, unalterable audit trail, showing who reviewed the document and when. This accountability is essential for compliance audits and resolving internal disputes over procedural adherence.
The following diagram illustrates how a document moves through an automated approval chain, from initial submission to sequential reviews and final execution.
This visual guide highlights how automation can enforce complex approval hierarchies, ensuring documents are reviewed by the right people in the right order, a process that includes automated reminders, which are a key part of effective communication. You can learn more about optimizing follow-up communication on tooling.studio.
10. Social Media Management and Posting
Automating social media management is another powerful business process automation example that boosts brand presence and engagement. This technology allows businesses to schedule posts across multiple platforms, monitor brand mentions, and analyze performance from a single dashboard. AI-driven systems can optimize posting times for maximum reach, suggest relevant content, and even handle common customer inquiries through automated responses.
This automation centralizes social media operations, ensuring a consistent brand voice and timely content delivery. For instance, platforms like Hootsuite and Sprout Social enable teams to manage complex content calendars and gain deep analytical insights, turning social media from a time-consuming task into a strategic, data-driven function. Sprout Social has shown that its automation features can increase team productivity by up to six times.
Strategic Breakdown
- Consistency and Scalability: Automation ensures a consistent posting schedule, which is crucial for building and maintaining an audience. It allows a small team, or even a single person, to manage a robust presence across numerous platforms without being overwhelmed, making social media strategy scalable as the business grows.
- Data-Driven Optimization: The true power of social media automation lies in analytics. By automatically tracking metrics like engagement rates, click-throughs, and follower growth, businesses can continuously refine their content strategy. This data-driven feedback loop helps focus efforts on content that delivers the highest ROI and aligns with business objectives.
Top 10 Business Process Automation Examples Comparison
| Automation Type | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invoice Processing Automation | Moderate to High; varied invoice formats | High-quality scanned docs, ERP integration | 70-80% reduction in processing time, cost savings | High-volume invoice handling in manufacturing, retail, healthcare | Reduces errors, faster payments, compliance |
| Customer Onboarding Automation | High; complex legacy integrations | Robust security, CRM integration | Onboarding time cut from weeks to hours | Financial services, SaaS, subscription services | Compliance ensured, improves customer experience |
| Employee Payroll Processing | High; multichannel system integration | HRIS, time tracking, banking systems | 80% faster payroll, error elimination | Large organizations, franchises | Accurate payments, compliance, reporting |
| Order Fulfillment & Inventory | High; multi-system and carrier integrations | Warehouse management systems, carriers | 60-80% faster order processing, fewer stockouts | Retail, e-commerce, omnichannel fulfillment | Improves accuracy, reduces costs, real-time tracking |
| Lead Generation & Qualification | Moderate; continuous scoring optimization | CRM, marketing platforms | 30-50% higher lead conversion rates | B2B sales, marketing teams | Increases sales efficiency, better lead quality |
| IT Help Desk & Ticket Routing | Moderate to High; requires knowledge base | Integration with monitoring tools | 60-70% faster first response time | IT support departments | Improves resolution consistency, SLA compliance |
| Expense Report Processing | Moderate; needs clear policies and training | Mobile apps, OCR, accounting systems | 75% reduction in processing time | Corporate finance, employee reimbursement | Reduces fraud, speeds reimbursement, cost savings |
| Email Marketing Campaigns | Moderate; ongoing content & data quality | CRM, e-commerce platforms | 50-80% increase in open rates | E-commerce, SaaS, customer engagement | Personalization at scale, higher ROI |
| Document Approval Workflows | Moderate to High; workflow design required | Document systems, e-signature tools | 60-80% faster approval cycles | Legal, procurement, corporate governance | Audit trails, transparency, remote approvals |
| Social Media Management & Posting | Moderate; needs continuous monitoring | Multiple social platforms | 70% reduction in manual posting time | Marketing teams, brand management | 24/7 presence, data-driven strategy |
Final Thoughts
Throughout this guide, we've explored a diverse set of business process automation examples, moving from abstract concepts to concrete, replicable strategies. The journey from manual invoice processing to streamlined IT help desks reveals a powerful, unifying theme: automation is not about replacing human ingenuity but augmenting it. It’s about reclaiming valuable time from repetitive, low-impact tasks and redirecting that energy toward strategic growth, innovation, and meaningful customer engagement.
The examples, from lead generation to document approval, demonstrate that the most effective automation starts small and stays focused. It targets specific pain points within existing workflows, often right where your team already collaborates: the inbox. By identifying these bottlenecks, you unlock cascading benefits that extend far beyond a single task, improving team morale, reducing operational costs, and increasing overall business agility.
Key Strategic Takeaways
As you consider implementing these ideas, remember these core principles:
- Start with the Friction: The best candidates for automation are not always the most complex processes. They are the ones causing the most daily friction, like tracking approvals in long email threads or manually creating tasks from client requests.
- Leverage Existing Tools: True efficiency isn't found by adding another standalone platform to your tech stack. It's discovered by enhancing the tools your team already uses daily, such as Gmail and Google Tasks. This approach minimizes the learning curve and maximizes adoption.
- Focus on Action, Not Just Information: The goal of automation is to trigger an action, assign a responsibility, and move work forward. Each example we covered, from sales pipeline management to social media scheduling, transforms static information into a dynamic, trackable task with clear ownership.
Strategic Insight: The most profound shift in productivity occurs when you stop using your inbox as a passive repository of information and transform it into an active command center for your entire workflow.
Your Next Steps Toward Automation
Mastering business process automation is an iterative journey, not a one-time project. Begin by selecting just one of the business process automation examples detailed in this article that resonates most with your team's current challenges. Map out the existing manual steps, identify the primary bottleneck, and apply the principles of centralized task management and streamlined communication.
The power lies in this incremental approach. By successfully automating one process, you create a blueprint for the next, building momentum and proving the tangible value of a more connected and efficient operational model. This is how sustainable, high-impact change is achieved.
Ready to turn these examples into your reality? Transform your Gmail inbox from a chaotic to-do list into a powerful, centralized hub for all your tasks and projects. See how Tooling Studio's extensions for Gmail and Google Tasks can help you implement these automation strategies today. Explore Tooling Studio and start streamlining your workflows.