
Top Sales Pipeline Examples to Boost Your Sales in 2025
Discover 6 effective sales pipeline examples to optimize your sales process. Find the best strategies to increase conversions in 2025!
Unlocking Sales Success with the Right Pipeline
A well-defined sales pipeline is essential for predictable revenue and growth. This listicle provides six sales pipeline examples to help you close more deals. Discover which model best suits your business, whether you're B2B, SaaS, or enterprise-focused. We'll cover the AIDA pipeline, the Salesforce 7-stage model, opportunity-focused pipelines, SaaS-specific models, account-based sales pipelines, and the solution selling pipeline. Learn the strengths and weaknesses of each, and see how these sales pipeline examples can boost your 2025 sales strategy.
1. AIDA Sales Pipeline
The AIDA (Awareness, Interest, Desire, Action) sales pipeline is a classic, linear sales funnel that uses customer journey psychology to guide prospects toward a purchase. This model breaks the sales process into four distinct stages: Awareness, Interest, Desire, and Action. It's particularly effective for B2C sales and marketing teams seeking a straightforward approach to lead conversion and shorter sales cycles, making it a strong contender amongst sales pipeline examples.
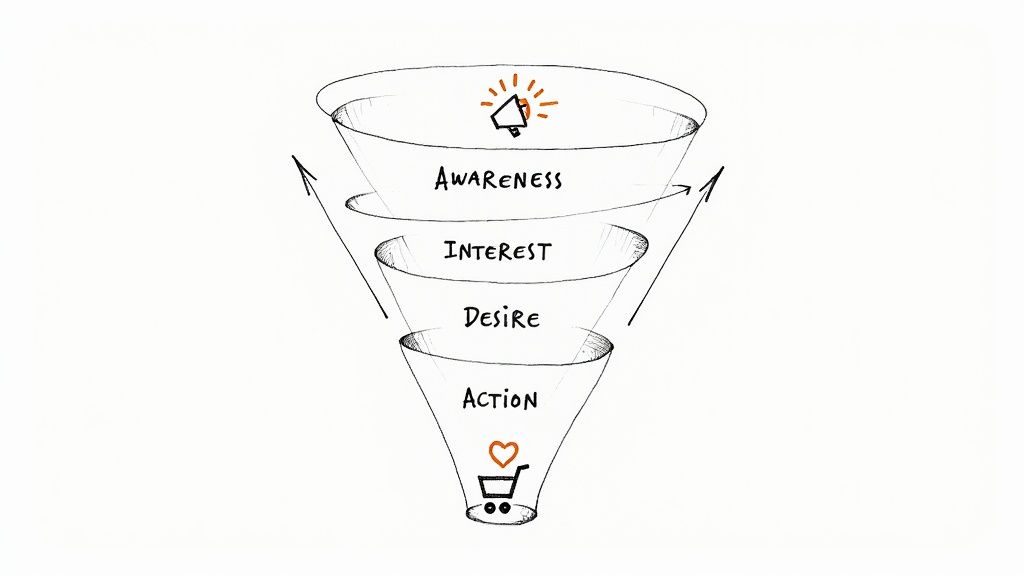
How AIDA Works:
The AIDA model functions as a step-by-step process:
- Awareness: The prospect becomes aware of your product or service, often through marketing efforts like advertising or social media.
- Interest: Once aware, the prospect develops an interest in learning more. This is where content marketing, such as blog posts or webinars, plays a crucial role.
- Desire: The prospect's interest evolves into a desire to own the product or service. Testimonials, case studies, and product demos can fuel this desire.
- Action: Finally, the prospect takes action by making a purchase or contacting your sales team. Clear calls to action and streamlined checkout processes are essential in this stage.
Examples of Successful AIDA Implementation:
- HubSpot: Implemented AIDA for their starter product lines and saw a 25% increase in conversion rates.
- Dollar Shave Club: Structured their direct-to-consumer sales approach around AIDA principles, achieving significant market penetration.
- Warby Parker: Successfully leveraged AIDA in their online eyewear sales process, driving customer acquisition and brand loyalty.
Tips for Implementing AIDA:
- Targeted Content: Create specific content tailored to each AIDA stage. For example, use engaging visuals for Awareness, informative blog posts for Interest, and compelling case studies for Desire.
- Automation: Use marketing automation to move prospects between stages based on their engagement. Track website visits, email opens, and content downloads to trigger personalized follow-ups.
- Metrics: Develop clear metrics to track progression through each stage, like conversion rates from Awareness to Interest, Interest to Desire, and Desire to Action. This provides insights into where the pipeline needs optimization.
- Tailored Messaging: Customize the messaging at each stage to address specific customer concerns and pain points. This resonates more effectively and fosters trust.
- Remarketing: Implement remarketing strategies to re-engage prospects who stall in the pipeline. Targeted ads and personalized emails can help nudge them towards the next stage.
When and Why to Use AIDA:
AIDA is ideal for businesses with shorter sales cycles, particularly in B2C markets. Its simplicity makes it easy to implement and understand, even for teams new to sales pipelines. It's also highly effective for products or services with a clear value proposition that can be readily communicated.
Pros:
- Simple to implement and understand
- Effective for shorter sales cycles
- Easy to train new sales team members
- Aligns well with marketing objectives
- Provides clear focus for each stage of customer engagement
Cons:
- May oversimplify complex B2B sales processes
- Doesn't account for post-purchase relationship management
- Linear format doesn't address variations in the sales cycle
- Less effective for relationship-based, long-term sales
- Minimal focus on qualification processes
Despite its limitations, the AIDA model's clarity and ease of implementation make it a valuable sales pipeline example, particularly for businesses focused on driving quick conversions and streamlined sales processes. It earns its place on this list by providing a foundational understanding of how to guide prospects through the sales funnel, a principle applicable even in more complex sales scenarios. While AIDA might not be the perfect solution for every business, its underlying principles of understanding and addressing customer needs at each stage of the journey are universally valuable.
2. Salesforce 7-Stage B2B Pipeline
The Salesforce 7-Stage B2B Pipeline is a robust sales pipeline example specifically designed for the complexities of business-to-business sales. Unlike simpler pipelines, it acknowledges the longer sales cycles, deeper relationship building, and multiple decision-makers often involved in B2B transactions. This method provides a structured framework from initial contact to closing the deal and beyond, enabling sales teams to manage complex deals effectively. It deserves a place on this list due to its comprehensive nature and adaptability for a variety of industries and B2B sales methodologies.
The following infographic visualizes the flow of the Salesforce 7-Stage B2B Pipeline, outlining each step in the process from Prospecting to Closed Won/Lost.
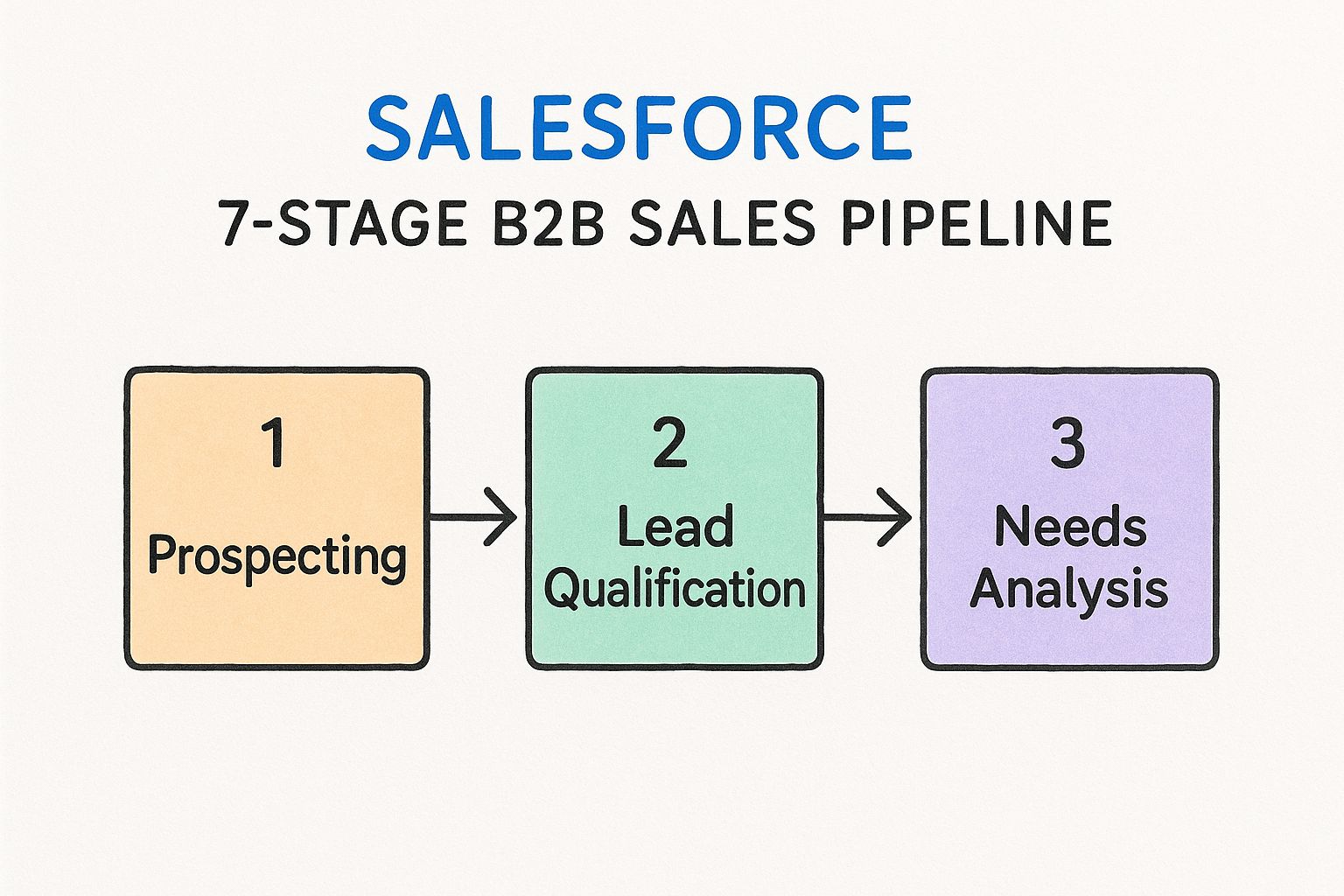
The infographic clearly illustrates the linear progression of a deal through the pipeline, highlighting the importance of qualification and needs analysis before moving to the value proposition and negotiation stages.
This pipeline operates through seven key stages: Prospecting, Lead Qualification, Needs Analysis, Value Proposition, Identify Decision Makers, Proposal/Price Quote, Negotiation/Review, and finally, Closed Won/Lost. The process begins with identifying potential clients (Prospecting) and then qualifying them based on factors like budget, authority, need, and timeline (BANT) or metrics, economic buyer, decision criteria, decision process, paper process, pain (MEDDIC). This emphasis on qualification is a core strength of this pipeline, helping to filter out unlikely prospects early on. After understanding the client's specific needs (Needs Analysis), a tailored Value Proposition is presented. The process continues with identifying key Decision Makers, submitting a Proposal/Price Quote, and engaging in Negotiation/Review. This structured approach ensures that all essential steps are covered, contributing to improved forecast accuracy and streamlined sales operations. Learn more about Salesforce 7-Stage B2B Pipeline
Features like built-in qualification frameworks (BANT, MEDDIC), integrated opportunity scoring, milestone-based progression criteria, and sophisticated forecasting capabilities make this pipeline particularly powerful. These features support data-driven decision-making and offer valuable insights into deal progress and potential revenue.
Pros:
- Comprehensive coverage of complex B2B sales processes.
- Strong emphasis on qualification to improve forecast accuracy.
- Detailed tracking capabilities for complex sales teams.
- Adaptable to different industries and sales methodologies.
- Supports cross-functional collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer success.
Cons:
- Can be overly complex for simple products or services.
- Requires significant setup and customization.
- May create administrative burden for sales representatives.
- Higher learning curve for new team members.
- Potentially expensive implementation with Salesforce licensing costs.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Adobe implemented this pipeline structure for their enterprise software sales division, improving forecasting accuracy by 35%.
- General Electric uses a modified version for their industrial equipment sales.
- Cisco Systems employs this pipeline structure across their global sales organization.
Tips for Implementation:
- Customize stage definitions to match your unique selling process.
- Define clear exit criteria for each pipeline stage.
- Train sales teams thoroughly on proper pipeline management.
- Regularly audit pipeline data for accuracy and sales rep accountability.
- Integrate marketing automation to help move deals through early stages.
The Salesforce 7-Stage B2B Pipeline is ideal for businesses with complex B2B sales cycles that require a structured and data-driven approach. While the setup and customization can be demanding, the long-term benefits in terms of improved forecasting, increased deal closure rates, and enhanced team collaboration often outweigh the initial investment. Consider this approach if your sales process involves multiple stakeholders, lengthy negotiations, and a high value per deal. This pipeline, popularized by figures like Marc Benioff and Aaron Ross, provides a proven framework for achieving predictable revenue and scaling B2B sales operations.
3. Opportunity-Focused Pipeline
This sales pipeline example, the Opportunity-Focused Pipeline, prioritizes quality over quantity. Instead of flooding the pipeline with every potential lead, it concentrates solely on qualified sales opportunities. This makes it an excellent choice for businesses with limited sales resources or those selling high-value products/services, allowing them to maximize their efforts where they are most likely to see a return. This approach is particularly relevant in today's market as businesses strive for efficiency and predictable revenue streams, making it a valuable addition to our list of sales pipeline examples.
How it Works:
The Opportunity-Focused Pipeline emphasizes pre-qualification before a lead even enters the pipeline. This means rigorously vetting prospects to ensure they align with your ideal customer profile (ICP) and have a genuine need and budget for your offering. The pipeline itself is typically shorter than others, often consisting of 5-6 stages focused on advancing the qualified opportunity towards closure. Key features include assigning probability percentages to each stage, enabling accurate revenue forecasting, and integration with lead scoring systems for efficient qualification.
Features and Benefits:
- Emphasis on pre-qualification: Filters out low-potential leads early in the process.
- Focused stages (typically 5-6): Streamlines the sales process for qualified opportunities.
- Probability percentages per stage: Allows for precise revenue forecasting.
- Revenue forecasting capabilities: Provides a clearer picture of potential revenue.
- Integration with lead scoring systems: Automates and standardizes the qualification process.
Pros:
- More accurate sales forecasting: By focusing on qualified opportunities, projections become more reliable.
- Efficient use of sales resources: Sales teams spend their time on high-potential prospects.
- Clearer view of realistic revenue potential: Reduces uncertainty in revenue projections.
- Higher conversion rates from pipeline to closed deals: Increased efficiency leads to a better close rate.
- Reduced time spent on unqualified leads: Eliminates wasted effort chasing dead ends.
Cons:
- May miss potential opportunities: Strict qualification criteria could exclude some viable prospects.
- Requires robust lead qualification process: Demands upfront investment in developing and implementing a robust system.
- Can create tension between marketing and sales: Disagreements might arise regarding lead quality and qualification criteria.
- Typically requires more sophisticated CRM configuration: Needs a CRM that supports probability tracking and integration with lead scoring.
- May not work well for businesses with very high volume, low-touch sales models: The rigorous qualification process may be impractical for high-volume sales.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Several high-performing companies have adopted the Opportunity-Focused Pipeline with notable success:
- Slack: Implemented this model for their enterprise sales team, reportedly increasing close rates by 40%.
- MongoDB: Uses an opportunity-focused pipeline for their database solutions sales.
- Workday: Employs this approach for their HCM and financial management software sales.
Actionable Tips:
- Develop a strong Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): Clearly define your target customer to guide qualification efforts.
- Implement lead scoring that aligns with your qualification criteria: Automate the identification of high-potential leads.
- Create clear definitions for what constitutes a qualified opportunity: Ensure consistency across the sales team.
- Regular pipeline reviews to validate opportunity quality: Ongoing monitoring maintains pipeline health and accuracy.
- Train sales teams to qualify out poor-fit prospects early: Empower sales representatives to make informed decisions.
Popularized By:
Influential figures in the SaaS world, including Jason Lemkin (SaaStr founder), Mark Roberge (former HubSpot CRO), and Jacco van der Kooij (founder of Winning by Design), have advocated for the Opportunity-Focused Pipeline.
When and Why to Use This Approach:
This sales pipeline example is best suited for businesses selling complex, high-value products or services with a longer sales cycle. If your sales team is struggling with limited resources or inaccurate forecasting, the Opportunity-Focused Pipeline offers a structured approach to improve efficiency and focus on deals most likely to close. This method is less suitable for businesses with a high-volume, transactional sales model where speed and lead quantity are paramount.
4. SaaS-Specific Pipeline Model
The SaaS-Specific Pipeline Model is a crucial sales pipeline example, specifically designed for Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies operating on a subscription-based revenue model. Unlike traditional sales pipelines, it acknowledges the unique journey of a SaaS customer, incorporating key stages like free trials, demos, proof of concept, and crucially, the potential for expansion revenue after the initial sale. This model recognizes that the sales process doesn't end with a closed-won deal; it's an ongoing relationship focused on customer success and growth. This focus on recurring revenue and customer lifetime value makes it a powerful tool for SaaS businesses looking to scale predictably.
Typically encompassing 6-8 stages from initial lead to closed-won, this model goes beyond traditional sales by including product-specific stages like trials and demos. It often incorporates technical validation phases to ensure the software effectively addresses the customer's needs. Furthermore, a key differentiator is the inclusion of post-sale expansion opportunities, reflecting the recurring revenue nature of SaaS. Many SaaS companies even separate their pipelines, creating one for new business acquisition and another specifically for expansion within existing accounts. This allows for more specialized tracking and management of each revenue stream.
Features and Benefits:
- Tailored to Subscription Models: Aligns perfectly with the recurring revenue nature of SaaS, focusing on customer lifetime value.
- Product-Led Growth: Supports product-led growth strategies by integrating trial and demo stages.
- Tracks Acquisition and Expansion: Effectively monitors both initial customer acquisition and subsequent expansion revenue.
- SaaS-Specific Metrics: Enables tracking of key SaaS metrics like Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), churn rate, and customer lifetime value.
- Cross-Functional Alignment: Fosters collaboration between sales, customer success, and product teams.
Pros and Cons:
- Pros: Highly effective for managing the complexities of SaaS sales, allowing for precise tracking and optimization of each stage.
- Cons: Can become complex, especially when managing both new business and expansion pipelines. May require custom CRM development and integrations with product analytics platforms.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Zoom: Leveraged this model during its rapid growth phase, effectively managing the influx of new customers while focusing on expansion within existing accounts.
- Dropbox: Uses a SaaS-specific pipeline, differentiating between freemium conversions and enterprise sales, tailoring the approach to each customer segment.
- Atlassian: Employs a version of this model, demonstrating its compatibility with product-led growth approaches.
Actionable Tips for Implementation:
- Integrate Product Usage Data: Connect product usage data directly into your pipeline for data-driven insights into customer behavior and potential expansion opportunities.
- Separate Pipeline Views: Create distinct pipeline views for new business and expansion efforts to manage each effectively.
- Smooth Handoffs: Develop clear handoff processes between sales and customer success teams to ensure a seamless customer experience.
- Monitor Conversion Rates: Track conversion rates at each stage, especially during trials and demos, to identify areas for improvement.
- Define Expansion Triggers: Establish clear triggers based on product usage and adoption metrics to proactively identify expansion opportunities.
Why This Model Deserves Its Place in the List:
The SaaS-Specific Pipeline Model is a critical sales pipeline example because it addresses the unique dynamics of the SaaS industry. Its focus on recurring revenue, customer lifetime value, and the integration of product usage data makes it an invaluable tool for SaaS businesses looking to achieve sustainable growth. Popularized by SaaS experts like David Skok, Tomasz Tunguz, and Jason Lemkin, this model has become a best practice for managing the complexities of subscription-based sales. This model's adaptability to both sales-led and product-led growth strategies further solidifies its place as an essential sales pipeline example for modern SaaS businesses.
5. Account-Based Sales Pipeline
The Account-Based Sales Pipeline stands out among sales pipeline examples due to its laser focus on targeting key accounts, rather than individual leads. This makes it particularly well-suited for complex B2B sales environments where deals involve multiple stakeholders, longer sales cycles, and require strategic coordination across different departments within the target organization. Instead of casting a wide net, this approach prioritizes deep engagement with a select group of high-value accounts, fostering stronger relationships and increasing the likelihood of closing large, complex deals.
This pipeline operates by organizing its stages around the targeted accounts themselves, tracking engagement with each individual stakeholder within those accounts. Features such as buying committee mapping and relationship strength indicators provide a comprehensive view of account penetration and facilitate more personalized, effective outreach. Often, account-based pipelines utilize tiered categorization (e.g., A, B, C accounts) to prioritize efforts and allocate resources strategically. This detailed approach allows sales teams to understand the nuances of each account, tailor their messaging, and coordinate outreach across multiple contacts within the organization. You can learn more about Account-Based Sales Pipeline and how it integrates with CRM systems.
Examples of successful implementation: Companies like Demandbase (using it for their own ABM platform), ServiceNow (for enterprise IT service management sales), and SAP (for their enterprise resource planning solutions) demonstrate the effectiveness of this model in complex, high-value enterprise sales.
When and why to use this approach: If your business targets large enterprise accounts with complex buying processes and high deal values, the Account-Based Sales Pipeline is likely a good fit. Its focus on strategic engagement and deep account understanding aligns perfectly with Account-Based Marketing (ABM) strategies. However, it's crucial to consider the resources required for implementation and ongoing management.
Pros:
- Aligns perfectly with Account-Based Marketing (ABM) strategies
- Effective for complex, high-value enterprise sales
- Provides a comprehensive view of account penetration
- Better suited for navigating complex buying committees
- Supports coordinated outreach across multiple contacts
Cons:
- More resource-intensive to implement and maintain
- Can be overkill for simpler sales processes
- Requires sophisticated CRM configuration and management
- Often needs dedicated operations support
- May be challenging to integrate with traditional lead-based marketing metrics
Tips for Implementation:
- Define clear Ideal Customer Profile (ICP) criteria: This helps focus your efforts on the most promising accounts.
- Map the buying committee roles at each account: Understand who the key decision-makers and influencers are.
- Track engagement metrics across the entire account: Don't just focus on individual interactions.
- Create account plans for high-value targets: Develop personalized strategies for each key account.
- Align marketing content strategy with account-based pipeline stages: Provide relevant and targeted content throughout the buyer journey.
The Account-Based Sales Pipeline represents a powerful approach for B2B sales, especially for those working within the Google Workspace environment and targeting enterprise-level clients. Its strategic focus and detailed tracking mechanisms provide the necessary tools to effectively manage complex sales cycles and build strong, lasting relationships with key accounts.
6. Solution Selling Pipeline
The Solution Selling Pipeline stands out among sales pipeline examples because it prioritizes addressing customer problems over simply pushing product features. This customer-centric approach makes it particularly effective for complex products or services aimed at solving specific business challenges. Instead of leading with a sales pitch, the focus is on understanding the customer's pain points and tailoring solutions to meet their unique needs. This method fosters stronger customer relationships and often results in larger deal sizes and longer-term partnerships.
This pipeline operates by guiding the sales process through several key stages:
- Problem Identification and Qualification: The initial stages concentrate on deeply understanding the customer's challenges and qualifying whether the offered solution is a viable fit. Effective discovery questions are crucial here.
- Discovery-Focused Early Pipeline Stages: Rather than presenting product features, the salesperson acts as a consultant, delving into the root causes of the customer's problems and exploring the potential impact of different solutions.
- Solution Configuration/Customization Phase: Based on the discovery phase, the solution is tailored or customized to address the specific needs identified. This might involve configuring software, bundling services, or developing a bespoke offering.
- Value Demonstration Milestones: Throughout the process, tangible value is demonstrated to the customer. This could involve presentations, pilot programs, or calculations showing potential return on investment (ROI).
- ROI Validation Stages: Before closing the deal, the projected ROI is validated, ensuring the customer understands the financial benefits of implementing the solution.
Why use a Solution Selling Pipeline?
This approach is ideal when dealing with complex sales, especially in competitive markets. By focusing on solutions, you differentiate yourself from competitors who may be simply pushing products. The in-depth understanding of customer needs also leads to stronger, more collaborative relationships.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
Large enterprises have effectively implemented Solution Selling Pipelines to drive sales of complex offerings. For instance, IBM uses this structure for its consulting services division, Accenture leverages it for digital transformation services, and Microsoft employs this approach for its enterprise cloud solution sales.
Pros:
- Customer-centric approach builds stronger relationships: Focusing on solving customer problems fosters trust and collaboration.
- Effective for complex, consultative sales processes: It allows for tailored solutions and in-depth value demonstration.
- Creates differentiation in competitive markets: Emphasizing solutions rather than products sets you apart.
- Tends to result in larger deal sizes: Comprehensive solutions often command higher prices.
- Often leads to longer-term customer relationships: Successful problem-solving builds loyalty and encourages repeat business.
Cons:
- Typically requires longer sales cycles: The in-depth discovery and solution development process takes time.
- Demands higher skill level from sales representatives: Salespeople need strong consultative and problem-solving skills.
- Requires deeper industry and business process knowledge: Understanding the customer's context is critical.
- More difficult to scale across large sales teams: Maintaining consistent methodology can be challenging.
- Can be challenging to maintain discipline in methodology: Requires rigorous adherence to the process.
Actionable Tips:
- Train sales teams to ask effective discovery questions: Uncovering the root causes of customer problems is crucial.
- Develop value calculation tools for each solution area: Quantify the benefits of your solutions.
- Create case studies demonstrating problem resolution: Show how you've helped other customers.
- Build solution playbooks for common customer challenges: Streamline the solution development process.
- Implement regular solution strategy reviews for pipeline opportunities: Ensure deals are progressing effectively.
Key Figures and Resources:
The Solution Selling methodology has been popularized by figures like Michael Bosworth (author of "Solution Selling"), Keith Eades (CEO of Sales Performance International), and the Miller Heiman Group (sales training organization). For those using Google Workspace and looking for ways to integrate CRM functionality within their workflow, Learn more about Solution Selling Pipeline might offer helpful insights into managing customer interactions and tracking progress within a familiar environment. This is particularly useful for project managers, team leads, sales representatives, and even individual professionals aiming for a unified approach to managing their tasks and client relationships.
This methodical and customer-centric approach deserves a prominent place among sales pipeline examples due to its effectiveness in complex sales environments. By focusing on solutions, building strong relationships, and demonstrating tangible value, the Solution Selling Pipeline can drive significant business growth and long-term success.
Sales Pipeline Models Comparison
| Pipeline Model | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIDA Sales Pipeline | Low - simple linear stages | Low - easy training & setup | Moderate - effective short sales | B2C sales, short sales cycles, marketing alignment | Easy to understand, clear stage focus |
| Salesforce 7-Stage B2B Pipeline | High - detailed stages, custom setup | High - significant setup and licensing | High - accurate forecasting & tracking | Complex B2B sales, enterprise, long cycles | Thorough qualification, detailed tracking |
| Opportunity-Focused Pipeline | Moderate - requires solid qualification | Moderate - CRM sophistication needed | High - better forecasting & conversion | High-value products, limited sales resources | Focus on qualified leads, efficient resource use |
| SaaS-Specific Pipeline Model | Moderate to High - includes trials and expansions | Moderate - may need custom CRM integration | High - tracks acquisition and expansion | SaaS companies, subscription models | Product-led growth, aligns sales & customer success |
| Account-Based Sales Pipeline | High - complex account and stakeholder mapping | High - resource-intensive, CRM dependent | High - deep account penetration & coordination | Complex B2B sales with multi-stakeholder decisions | Strong alignment with ABM, coordinated outreach |
| Solution Selling Pipeline | High - requires skilled reps & consultative process | High - training and expertise investment | High - larger deals, strong relationships | Complex, consultative sales, problem-solving products | Customer-centric, value demonstration |
Power Up Your Sales Process Today
This article explored a diverse range of sales pipeline examples, from the classic AIDA model to more specialized approaches like the SaaS-Specific and Account-Based pipelines. We've seen how the Salesforce 7-Stage B2B pipeline offers a robust framework, while the Opportunity-Focused and Solution Selling pipelines emphasize specific aspects of the sales journey. The key takeaway is that no single pipeline fits all. Choosing the right model depends on understanding your unique business needs, sales cycle length, and target audience.
Mastering these concepts empowers you to not just manage your sales process, but to actively shape and optimize it for maximum impact. By implementing a well-defined pipeline, you gain clearer visibility into your sales activities, can identify potential bottlenecks, and forecast revenue more accurately. Sometimes, finding the right approach requires a fresh perspective. For more strategies on tackling challenges and finding innovative solutions, explore resources on creative problem solving. Ultimately, a well-structured sales pipeline translates to stronger customer relationships, increased conversion rates, and sustainable business growth.
Looking to streamline your sales process within the Google Workspace ecosystem? Tooling Studio offers a powerful Sales CRM (currently in beta) designed to seamlessly integrate with your existing tools, including Google Contacts, giving you a centralized platform to manage your chosen sales pipeline. Visit Tooling Studio to learn more and supercharge your sales efforts today.