
Top 8 Prioritization Techniques to Boost Productivity
Discover key prioritization techniques to manage tasks effectively and achieve goals. Master methods like Eisenhower Matrix and MoSCoW today!

Overwhelmed by Your To-Do List? Take Charge with These Techniques!
Drowning in tasks? Effective prioritization is key to productivity and achieving goals. This article presents eight proven prioritization techniques to regain control of your workflow. Learn how to apply the Eisenhower Matrix, MoSCoW Method, RICE Scoring, Kano Model, Value vs. Effort Matrix, Weighted Scoring Model, Story Mapping, and Opportunity Scoring. These techniques provide practical strategies for project managers, team leads, sales representatives, freelancers, and anyone using Google Workspace to conquer their to-do list and maximize their time. Master these prioritization techniques and reclaim your focus.
1. Eisenhower Matrix (Urgent-Important Matrix)
The Eisenhower Matrix, also known as the Urgent-Important Matrix, is a powerful prioritization technique that helps individuals and teams effectively manage their time and focus on what truly matters. This method provides a simple framework for categorizing tasks based on two key criteria: urgency and importance. By visualizing these criteria, the matrix helps you distinguish between tasks that demand immediate attention and those that contribute to long-term goals. This distinction is crucial for reducing reactive behavior and promoting proactive, strategic thinking, earning its place as a top prioritization technique.
The matrix consists of four quadrants:
- Quadrant 1: Do First (Urgent & Important): These tasks are both time-sensitive and crucial for achieving your objectives. Examples include dealing with crises, meeting deadlines, and handling pressing problems.
- Quadrant 2: Schedule (Important but Not Urgent): This quadrant houses activities that contribute significantly to your long-term goals but don't have an immediate deadline. These are often neglected but are crucial for long-term success. Examples include planning, relationship building, skill development, and preventative maintenance.
- Quadrant 3: Delegate (Urgent but Not Important): These tasks are urgent but don't contribute significantly to your goals. They often create the illusion of importance due to their urgency. Examples include attending some meetings, responding to certain emails, and dealing with interruptions. Whenever possible, these tasks should be delegated.
- Quadrant 4: Eliminate (Neither Urgent nor Important): These tasks are time-wasters that neither contribute to your goals nor require immediate attention. Examples include busywork, trivial tasks, and excessive social media consumption. These should be eliminated ruthlessly to free up time for more valuable activities.
The Eisenhower Matrix promotes strategic thinking by encouraging you to focus on Quadrant 2 activities. By dedicating sufficient time to planning, learning, and proactive work, you can prevent many Quadrant 1 crises from arising in the first place.
Successful Implementation Examples:
- CEOs: CEOs can use the Eisenhower Matrix to balance strategic planning (Quadrant 2) with addressing urgent operational issues (Quadrant 1), ensuring they dedicate sufficient time to both short-term needs and long-term vision.
- Project Managers: Project managers can categorize feature requests and bug fixes. Critical bugs fall into Quadrant 1, while planning future sprints falls into Quadrant 2. Less critical bugs might be delegated (Quadrant 3), while unnecessary feature requests might be eliminated (Quadrant 4).
- Students: Students can use the matrix to balance coursework deadlines (Quadrant 1), study time for exams (Quadrant 2), attending club meetings (Quadrant 3), and excessive video game playing (Quadrant 4).
Actionable Tips for Using the Eisenhower Matrix:
- Regular Review: Review and update your matrix weekly, or even daily, to adjust to shifting priorities.
- Focus on Quadrant 2: Aim to spend 60-70% of your time on Quadrant 2 activities to proactively work towards your long-term goals.
- Define Criteria: Establish clear criteria for what constitutes "urgent" and "important" to avoid subjective classifications.
- Visual Clarity: Color-code the quadrants for better visual organization and quicker decision-making.
Pros:
- Simple and intuitive to understand and implement.
- Helps reduce reactive behavior and promotes proactive planning.
- Focuses on strategic priorities and long-term goals.
- Facilitates effective delegation decisions.
Cons:
- Subjective determination of urgency and importance can be challenging.
- May oversimplify complex prioritization scenarios with numerous interdependent tasks.
- Requires regular reassessment as priorities can shift frequently.
- Can be difficult to apply to tasks with dependencies.
The following infographic visualizes the core concepts of the Eisenhower Matrix, highlighting the relationships between urgency, importance, and the resulting action categories.
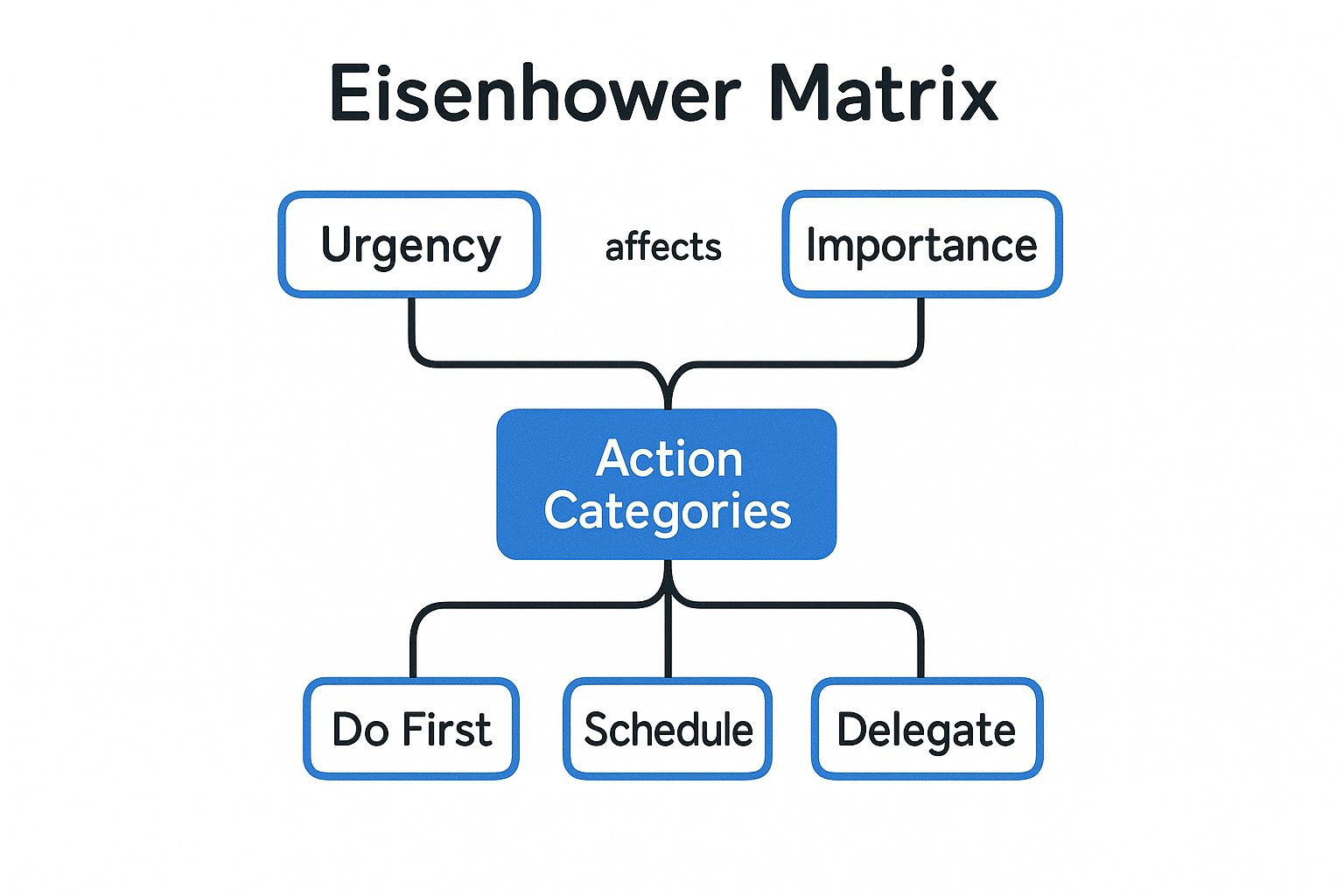
The infographic clearly illustrates how the intersection of urgency and importance dictates the appropriate action for each task, from immediate action to elimination. The central concept of "Action Categories" branches out based on the binary classification of urgency and importance, guiding users towards the most effective approach for each task.
The Eisenhower Matrix, popularized by Dwight D. Eisenhower and Stephen Covey, is a valuable tool for anyone seeking to improve their time management and prioritization skills. By consistently applying this technique, individuals and teams can gain greater control over their workload, reduce stress, and achieve meaningful progress towards their goals. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it especially beneficial for project managers, team leads, and individual professionals working within Google Workspace or other productivity environments.
2. MoSCoW Method
The MoSCoW method is a powerful prioritization technique that brings clarity and structure to project planning and resource allocation. It helps teams decide what absolutely must be done, what should ideally be included, what could be added if time and resources allow, and what won't be addressed in the current timeframe. This simple yet effective framework facilitates stakeholder alignment and prevents scope creep by clearly defining priorities. The MoSCoW method, originally developed for software development within the Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) framework, has proven its adaptability across various industries, from marketing to government projects. Its value lies in its ability to streamline decision-making and ensure everyone is on the same page regarding what truly matters.
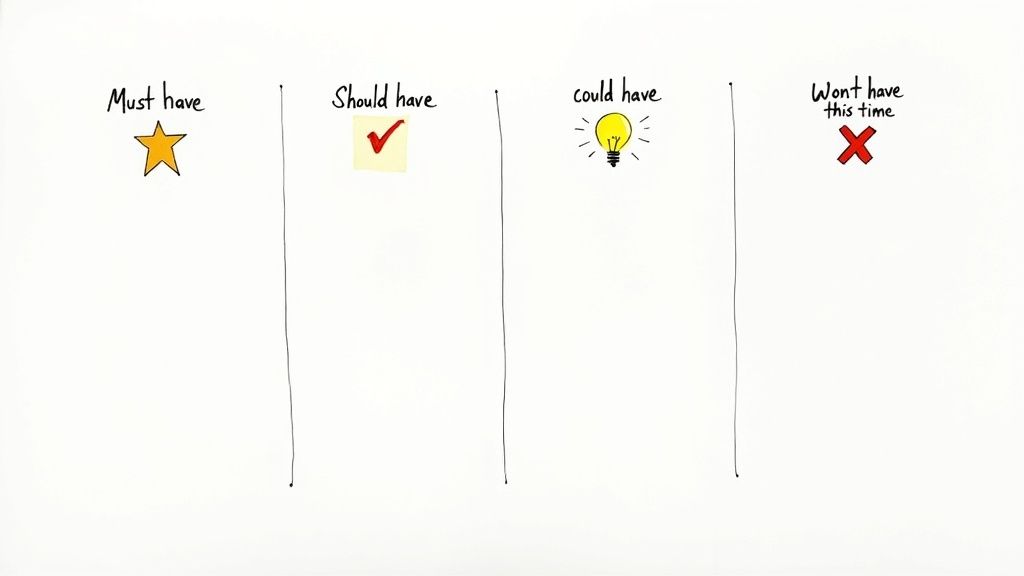

The MoSCoW method categorizes requirements or tasks into four distinct priority groups:
Must have (M): These are the non-negotiable requirements, crucial for the project's success. Without these elements, the project is considered incomplete or fundamentally flawed. Examples include core features of a software release, legal compliance requirements, or essential components of a marketing campaign.
Should have (S): These are important features or tasks that add significant value but are not essential for launch or completion. While their absence might impact the overall user experience or project outcome, the project can still function without them. These might be secondary features, performance enhancements, or additional marketing materials.
Could have (C): These are desirable features or tasks that would be nice to have if time and resources permit. They offer additional value but are not critical. Often, these items are the first to be cut if the project faces time or budget constraints. Think of these as "bonus" features, optional reports, or supplementary marketing activities.
Won't have this time (W): These are features or tasks that have been explicitly excluded from the current scope. This doesn't mean they are unimportant, but rather that they are deferred to a later phase or a different project altogether. Documenting these items prevents them from being forgotten and provides a starting point for future planning.
The MoSCoW method's effectiveness lies in its collaborative nature. It encourages active stakeholder participation, fostering consensus and buy-in. By involving key stakeholders in the categorization process, teams can ensure that everyone understands and agrees on the prioritization logic. This shared understanding minimizes misunderstandings and reduces the likelihood of conflicts later on. For Google Workspace users, this collaborative aspect can be further enhanced through shared documents and real-time collaboration tools, ensuring everyone is involved in the prioritization process.
Successful Implementations: Companies like Spotify utilize the MoSCoW method for product roadmap prioritization, ensuring that new features align with user needs and business goals. Government IT projects often employ this technique during requirements gathering to effectively manage complex stakeholder needs and prioritize essential functionalities. For sales teams using a CRM within Google Workspace, the MoSCoW method can help prioritize leads, opportunities, and sales activities, focusing efforts on the most promising prospects and deals.
Actionable Tips for Effective Use:
- Limit 'Must haves': Aim to keep 'Must haves' to around 60% of your available capacity. Overloading the 'Must have' category can lead to unrealistic deadlines and project overload.
- Timeboxing: Use time constraints to create urgency for decisions. This encourages stakeholders to focus on what's truly essential.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Involve all key stakeholders in the categorization process to ensure buy-in and alignment.
- Revisit 'Won't haves': Regularly review the 'Won't have' list to reassess priorities and consider deferred items for future inclusion.
Pros and Cons:
Pros: The MoSCoW method excels at stakeholder alignment, preventing scope creep, and facilitating clear communication of priorities. It is adaptable across different industries and project types.
Cons: It can sometimes lead to an overabundance of 'Must haves' if not carefully managed. It requires strong facilitation skills to guide the categorization process effectively. Quantifying the business value differences between categories can also be challenging.
The MoSCoW method earns its place amongst prioritization techniques because it provides a structured and collaborative approach to decision-making. By clearly defining priorities and facilitating stakeholder consensus, it helps teams focus on what truly matters, maximizing project success and minimizing wasted effort. This makes it particularly relevant for project managers, team leads, and even individual professionals working within the Google Workspace environment, enabling them to streamline their workflows and prioritize tasks effectively.
3. RICE Scoring Model
The RICE Scoring Model is a powerful prioritization technique that brings objectivity and data-driven decision-making to your projects. It's particularly valuable when you're facing a backlog of potential initiatives and need a clear, quantifiable way to determine which ones to tackle first. Instead of relying on gut feeling or loudest voice in the room, RICE provides a framework for evaluating options based on four key factors: Reach, Impact, Confidence, and Effort. This allows you to compare seemingly disparate projects on a level playing field and prioritize those with the highest potential return on investment. For project managers, team leads, and even individual professionals juggling multiple tasks, RICE offers a structured approach to making informed choices about where to focus your limited resources.
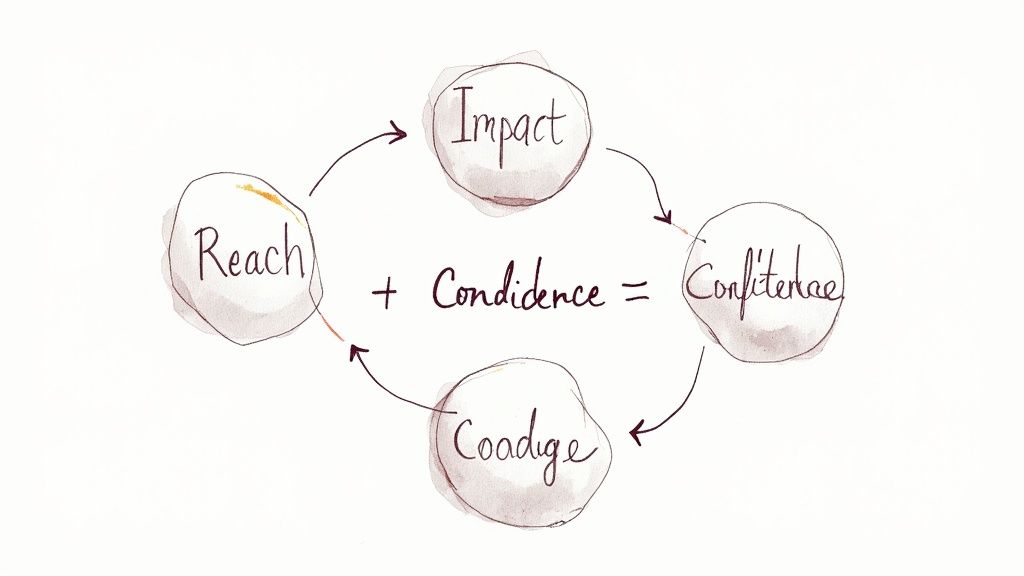
The RICE score itself is calculated using a simple formula: (Reach × Impact × Confidence) / Effort. Let's break down each of these components:
Reach: This represents the number of people who will be affected by the initiative within a defined timeframe. For a new software feature, this could be the number of users who will access it. For a marketing campaign, it might be the number of people who see your ad. It's crucial to use consistent units of measurement (e.g., users per month, page views per week) when comparing different initiatives.
Impact: This measures how much each person affected will benefit from the initiative. Impact is inherently more subjective than Reach, but you can still quantify it using a scale. For instance, you might use a scale of 1-3, where 3 represents a massive impact, 2 a moderate impact, and 1 a minimal impact. Defining clear criteria for each level on your scale is essential for consistency.
Confidence: This factor accounts for the uncertainty inherent in your estimates. How confident are you in your projections for Reach and Impact? Express this as a percentage. If you're very confident in your numbers, use a higher percentage (e.g., 90%). If you're less certain, use a lower percentage (e.g., 50%). This prevents over-prioritizing initiatives based on overly optimistic projections.
Effort: This represents the total work required to complete the initiative. This can be measured in person-hours, days, weeks, or whatever unit makes sense for your team. Accurate effort estimation is crucial for the RICE model to be effective.
By multiplying Reach, Impact, and Confidence, and then dividing by Effort, you get a single RICE score for each initiative. The higher the score, the higher the priority. This quantitative approach allows for objective comparison and ranking of various projects, even across different departments or project types.
The RICE scoring model has seen successful implementation across various organizations. Intercom, a customer messaging platform, famously uses RICE for product development prioritization. Marketing teams utilize it to evaluate campaign opportunities, weighing the potential reach and impact against the resources required. SaaS companies find it valuable for prioritizing product improvements, ensuring they focus on features that deliver the most value to the largest number of users. Even fast-paced startups like Airbnb and Uber have leveraged the RICE model to navigate their rapid growth and prioritize initiatives effectively.
While RICE offers many advantages, including reduced bias, clear numerical rankings, and data-driven prioritization, it also has some limitations. It relies heavily on accurate data estimation, and if your inputs are flawed, your output will be as well. It can also give a false sense of precision, particularly when dealing with uncertain estimates. Furthermore, the model may not adequately capture strategic or qualitative factors that are difficult to quantify. Finally, scoring numerous items can be time-consuming.
To effectively utilize the RICE scoring model, consider these tips: Use consistent scales for Reach, Impact, and Effort across all evaluations. Involve cross-functional teams in the scoring process to gain diverse perspectives and improve estimation accuracy. Don't treat the scores as absolute truth; combine them with qualitative considerations and strategic alignment for final decision-making. Finally, re-score periodically as new data emerges and circumstances change.
The RICE scoring model deserves its place on this list of prioritization techniques because it provides a practical, data-driven framework for making objective decisions. By forcing you to consider multiple factors and quantify your assumptions, RICE helps eliminate guesswork and ensures you're focusing on the initiatives with the highest potential impact. For teams using Google Workspace, the collaborative nature of the platform makes it ideal for implementing RICE scoring, facilitating shared spreadsheets and discussions around prioritization. Whether you’re managing a complex project, evaluating sales leads, or simply trying to organize your individual tasks, RICE offers a valuable tool for prioritizing effectively and maximizing your impact.
4. Kano Model
The Kano Model is a powerful prioritization technique that goes beyond simply listing features and ranking them by perceived importance. It offers a nuanced approach to understanding customer needs and desires, allowing product development teams to make strategic decisions about which features to prioritize. This method deserves its place on this list due to its customer-centric approach and ability to drive product development towards features that truly resonate with users, leading to higher satisfaction and competitive advantage.
This model, developed by Professor Noriaki Kano, categorizes customer preferences into five distinct categories:
Must-be Quality (Basic Expectations): These are the fundamental features that customers expect as a given. Their presence doesn't necessarily increase satisfaction, but their absence creates significant dissatisfaction. Think of power windows in a modern car – no one raves about them, but their absence would be a major drawback. Meeting these needs is crucial for simply being in the game.
One-dimensional Quality (Performance Features): These features directly correlate with customer satisfaction. The better the performance, the higher the satisfaction. For example, a faster internet connection or a longer battery life on a laptop. These are the features customers actively compare and evaluate when making purchasing decisions.
Attractive Quality (Delighters): These unexpected features go above and beyond customer expectations, creating a strong positive emotional response. They are often innovative and differentiate a product from its competitors. Think of the first introduction of a backup camera in a car – it wasn't expected, but it quickly became a highly desirable feature. Focusing on these features can create a significant competitive advantage.
Indifferent Quality (No Impact): These features neither increase nor decrease customer satisfaction. They are essentially neutral and should be considered low priority. An example might be the color of a stapler – while some may have a preference, it’s unlikely to significantly impact their overall satisfaction with the product.
Reverse Quality (Dissatisfiers): These features actually cause dissatisfaction when present. They often represent an over-complication or a misinterpretation of customer needs. An overly complex user interface for a simple task could fall into this category. Identifying and eliminating these features is crucial for improving customer satisfaction.
The Kano Model helps teams understand the non-linear relationship between features and satisfaction. Simply adding more features doesn't guarantee increased satisfaction. In fact, focusing on the wrong types of features can lead to bloated products, increased development costs, and ultimately, dissatisfied customers.
How It Works:
The Kano Model relies heavily on customer feedback. Through carefully designed surveys, customers are asked to evaluate each feature twice: once assuming the feature is present, and once assuming it is absent. Their responses are then mapped onto the five categories. This process provides invaluable insights into how customers truly perceive the value of each feature.
Examples of Successful Implementation:
- Toyota: Toyota has long been known for its focus on Must-be Quality and One-dimensional Quality, ensuring their vehicles are reliable and perform well. However, they also strategically introduce Attractive Quality features to differentiate their models and enhance customer loyalty.
- Apple: Apple's success with the iPhone can be attributed, in part, to their ability to identify and deliver Attractive Quality features. Features like the intuitive touchscreen interface and the App Store initially delighted users and set the iPhone apart from the competition.
- Software Companies: Microsoft utilizes the Kano Model to prioritize features for software like Microsoft Office, understanding which features are essential (Must-be), which enhance productivity (One-dimensional), and which could delight users with unexpected functionality (Attractive).
Actionable Tips for Using the Kano Model:
- Conduct Regular Customer Surveys: Customer preferences evolve over time. Regular surveys ensure your categorization remains accurate and reflects current market needs.
- Focus Innovation Efforts on Attractive Quality Features: These features provide the greatest opportunity for differentiation and creating a loyal customer base.
- Ensure Must-be Quality Features are Table Stakes: Never neglect the basics. Failing to meet these fundamental expectations can severely damage your product's reputation.
- Monitor Feature Migration: Features can shift categories over time. What was once a delighter can become a basic expectation. Regularly reassess your categorization to maintain accurate prioritization.
When and Why to Use the Kano Model:
The Kano Model is particularly valuable in situations where:
- You are developing a new product and need to prioritize features.
- You are looking to improve an existing product and need to understand which features are truly valuable to customers.
- You are trying to differentiate your product from competitors.
- You want to avoid over-engineering your product by focusing on the features that matter most to customers.
While implementing the Kano Model requires dedicated customer research and analysis, the insights gained can significantly improve product development decisions, leading to greater customer satisfaction, increased market share, and a stronger competitive edge. This makes it a valuable prioritization technique for any project manager or team lead seeking to deliver products that truly resonate with their target audience.
5. Value vs. Effort Matrix (Impact-Effort Matrix)
The Value vs. Effort Matrix, also known as the Impact-Effort Matrix, is a powerful prioritization technique that helps individuals and teams make informed decisions about which initiatives to pursue. It's a visual tool that plots tasks and projects on a two-dimensional grid based on their potential value (or impact) and the effort required to complete them. This simple yet effective method provides a clear framework for strategic decision-making, especially when resources are limited. This makes it an invaluable tool for project managers, team leads, and anyone juggling multiple responsibilities, particularly within fast-paced environments like sales, IT, or consulting, where effective prioritization is crucial for success.
The matrix is divided into four quadrants, each representing a different strategic priority:
- Quick Wins (High Value, Low Effort): These are the low-hanging fruit – initiatives that offer significant value with minimal effort. Focusing on these tasks first can generate early momentum and boost team morale. Examples include implementing a small software update with a significant impact on user experience or automating a repetitive administrative task.
- Major Projects (High Value, High Effort): These initiatives offer substantial value but require significant investment in time and resources. They are strategically important but should be planned and executed carefully. Examples might include developing a new product line, overhauling a core IT system, or launching a major marketing campaign.
- Fill-ins (Low Value, Low Effort): These tasks are easy to complete but offer minimal value. While they might be necessary, they shouldn't be prioritized over higher-impact activities. Examples might include routine data entry, minor website updates, or filing paperwork.
- Thankless Tasks (Low Value, High Effort): These are activities that require significant effort but yield little value. They should be avoided whenever possible or, if unavoidable, streamlined or delegated. Examples might include generating a complex report that is rarely used or troubleshooting a legacy system that's slated for replacement.
The power of the Value vs. Effort Matrix lies in its visual representation. By plotting initiatives on the grid, you gain a clear overview of your options and can easily identify which tasks offer the best return on investment. Learn more about Value vs. Effort Matrix (Impact-Effort Matrix)
How does it work in practice? Let's say a marketing team is brainstorming campaign ideas. They could use the matrix to plot each idea based on its potential impact (e.g., leads generated, brand awareness) and the effort required (e.g., budget, time). This allows them to quickly identify high-impact, low-effort campaigns (Quick Wins) and prioritize them accordingly. Similarly, an IT department could use the matrix to prioritize system improvements, weighing the potential performance gains against the complexity of implementation. Consulting firms often utilize this matrix to visually represent client recommendations, clearly highlighting which strategic initiatives offer the greatest potential returns for the least effort. Agile teams also frequently leverage this matrix for prioritizing user stories, ensuring that the most valuable features are tackled first.
Why is this technique valuable for prioritization? The Value vs. Effort Matrix provides a balanced approach, considering both impact and feasibility. It encourages strategic thinking by forcing you to evaluate the potential return of each initiative. It also helps to identify quick wins, which can generate momentum and build confidence for tackling larger projects.
Here are some actionable tips for using the Value vs. Effort Matrix effectively:
- Collaborative Plotting: Conduct team workshops to ensure diverse perspectives and buy-in. This collaborative approach leads to a more comprehensive understanding of both value and effort.
- Defined Criteria: Establish clear criteria for assessing value and effort. Use quantifiable metrics whenever possible (e.g., revenue increase, time saved). This removes subjectivity and promotes consistent evaluation.
- Start with Quick Wins: Prioritize tasks in the Quick Wins quadrant to build momentum and demonstrate early success.
- Regular Reassessment: The business environment is dynamic. Regularly reassess the positioning of initiatives on the matrix as conditions change, priorities shift, or new information becomes available.
Pros of using the Value vs. Effort Matrix:
- Intuitive Visual Representation: Easy to understand and communicate to stakeholders.
- Balanced Approach: Considers both impact and feasibility.
- Identifies Quick Wins: Helps generate early momentum and build confidence.
- Avoids Low-Value Activities: Highlights tasks that should be avoided or streamlined.
Cons of using the Value vs. Effort Matrix:
- Subjective Assessment: Estimating value and effort can be subjective, even with defined criteria.
- Oversimplification: May oversimplify complex initiatives with multiple dependencies.
- Strategic Timing: Doesn't explicitly account for strategic timing or deadlines.
- Quick Win Bias: Can lead to overemphasis on quick wins at the expense of strategically important, but high-effort projects.
Despite these potential drawbacks, the Value vs. Effort Matrix remains a valuable prioritization technique for individuals and teams across various industries and functions. Its simplicity, combined with its ability to balance impact and feasibility, makes it an essential tool for effective decision-making in today's complex business environment.
6. Weighted Scoring Model
The Weighted Scoring Model is a powerful prioritization technique that brings objectivity and structure to complex decisions. It's a quantitative approach that allows you to evaluate different options against a set of pre-defined criteria, each weighted according to its relative importance. This method provides a clear and transparent way to compare alternatives, especially when multiple stakeholders are involved and various factors need consideration. It moves beyond gut feelings and subjective opinions, offering a data-driven approach to prioritization. This makes it particularly valuable for project managers, team leads, and anyone working in a fast-paced environment where informed decisions are critical.
How does it work? First, identify the criteria relevant to your decision. For example, if you're selecting a new software vendor, criteria might include cost, functionality, integration capabilities, and vendor reputation. Next, assign a weight to each criterion, reflecting its importance. For instance, functionality might be weighted higher than cost if your primary concern is the software's features. Then, score each option against each criterion using a numerical scale (e.g., 1-5, 1-10). Finally, multiply each score by its corresponding weight and sum these weighted scores for each option. The option with the highest total weighted score represents the most favorable choice.
The Weighted Scoring Model's strength lies in its multi-criteria evaluation framework. It allows you to consider a diverse range of factors, ensuring a more holistic assessment than simpler prioritization methods. The customizable weighting system allows you to tailor the model to specific project needs and stakeholder priorities. Numerical scoring provides an objective basis for comparison, minimizing bias and promoting transparency. This structured approach makes the decision-making process auditable, allowing you to justify your choices based on clear evidence. This is particularly useful in environments like government procurement or enterprise software selection, where transparency and accountability are paramount.
The Weighted Scoring Model has found successful application in diverse fields. Government procurement processes often use this model to ensure fair and transparent vendor selection. Large enterprises like IBM leverage it for software vendor evaluation. Investment portfolio optimization and even university admission processes benefit from this structured approach.
While the Weighted Scoring Model offers significant advantages, it's crucial to be aware of its limitations. Setting up the model and evaluating options can be time-consuming, especially with numerous criteria or options. Reaching consensus on criteria and their respective weights can be challenging and potentially controversial. The numerical scoring system, while promoting objectivity, can also create a false sense of precision. Finally, it's important to document the rationale behind weighting decisions to maintain transparency and facilitate future review. Learn more about Weighted Scoring Model and how it can fit into your existing workflows within Google Workspace.
To effectively utilize the Weighted Scoring Model, consider these tips: involve stakeholders in defining criteria and weights to ensure buy-in and address diverse perspectives; limit the number of criteria to 5-10 to avoid unnecessary complexity; test the model’s sensitivity by adjusting weights and observing the impact on the final ranking; and meticulously document the rationale for all weighting decisions to maintain transparency and facilitate future audits.
The Weighted Scoring Model deserves a place on this list of prioritization techniques because it provides a robust and transparent framework for navigating complex decisions. By offering a structured, data-driven approach, it helps reduce bias, promote consensus, and ultimately, leads to more informed and defensible choices. For project managers, team leads, sales teams, and even individual professionals using Google Workspace, the Weighted Scoring Model offers a valuable tool for prioritizing tasks, projects, and opportunities, leading to increased productivity and better outcomes. It's particularly relevant for those seeking optimized to-do lists and efficient project management within the Google Workspace ecosystem.
7. Story Mapping: Visualizing the User Journey for Effective Prioritization
Story mapping is a powerful prioritization technique that goes beyond simple backlog grooming. It provides a visual and holistic view of the user journey, allowing teams to prioritize features based on their contribution to the overall user experience. This method deserves its place on this list because it tackles prioritization from a user-centric perspective, ensuring that the most valuable features are delivered first. This is particularly crucial for project managers and team leads using Google Workspace, as well as small and medium-sized businesses, sales teams, and even individual professionals looking for unified and effective task management. By understanding the entire user flow, teams can make informed decisions that maximize impact and deliver a cohesive product experience.
Instead of simply listing features in a prioritized order, story mapping arranges user stories along two dimensions. Horizontally, stories are organized according to the steps in the user journey or workflow. Vertically, they are prioritized based on their importance and value. This two-dimensional representation offers a comprehensive overview of the entire user experience, revealing dependencies, gaps, and opportunities for optimization. Imagine planning a road trip. A simple prioritized list might tell you the cities you need to visit in order of importance, but a map shows you the route, the connections, and the overall journey. Similarly, a story map provides the context for individual features within the broader user experience, facilitating better prioritization decisions.
Story mapping offers several key features: a two-dimensional visual representation that's easy to understand, user journey-centric organization, a hierarchical story structure for breaking down complex features, and seamless integration with release planning. This makes it an incredibly valuable tool for anyone, from Google Workspace administrators seeking productivity extensions to sales representatives needing an integrated CRM. By visualizing the user flow, teams can identify which features are critical for a minimum viable product (MVP) and which can be added in later releases. This hierarchical approach allows for flexible planning and adaptation to changing market demands.
The benefits of using story mapping are numerous. It maintains a strong user experience focus throughout the development process, ensuring that the final product meets user needs effectively. The visual nature of the map reveals potential gaps in the user journey, allowing teams to identify missing features or areas for improvement. Furthermore, story mapping facilitates release planning by clearly outlining the features required for each release milestone. It also promotes a shared understanding of the project across different teams, from development and design to marketing and sales.
However, story mapping also has its drawbacks. Managing large backlogs can make the map complex and unwieldy. The map requires ongoing maintenance to reflect changes in requirements or priorities. It may not be suitable for all types of products, particularly those with highly unpredictable or rapidly changing user needs. Finally, successful story mapping sessions often require experienced facilitation to guide the process and ensure effective collaboration.
Many successful companies have employed story mapping in their product development process. Spotify, for example, is known for its user-centric approach, and story mapping has likely played a role in shaping their product roadmap. E-commerce companies use it to map the entire shopping experience, from browsing to checkout, and prioritize features that enhance conversion rates. SaaS companies like Atlassian utilize story mapping for planning feature releases and ensuring a cohesive user experience across their platforms. Even mobile app development teams benefit from this technique to visualize user flows and prioritize key functionalities.
To effectively implement story mapping, start with identifying high-level user activities and arrange them horizontally. Then, use physical or digital sticky notes to represent user stories and place them vertically beneath the corresponding activity, ordered by priority. It’s important to include diverse perspectives in mapping sessions, involving representatives from different departments and even end-users if possible. Regularly validate the story map with actual user research to ensure it accurately reflects user needs and expectations. Learn more about Story Mapping can provide further insights into effectively integrating this technique into your workflow.
Story mapping, as popularized by Agile consultant and author Jeff Patton, has become a valuable tool in the Agile software development community. It’s a powerful prioritization technique that helps teams understand the user experience holistically and make informed decisions about which features to develop first. By focusing on the user journey, story mapping ensures that the final product is not just a collection of features but a cohesive and valuable experience for the user. Using this method helps teams focus on what truly matters, delivering a product that not only meets user needs but also achieves business goals. This is essential for anyone working within Google Workspace, seeking streamlined project management and improved productivity across the board.
8. Opportunity Scoring: Unearthing Hidden Gems for Product Improvement
Opportunity scoring is a powerful prioritization technique that moves beyond simply asking customers what they want. Instead, it delves into the gap between what customers find important and how satisfied they are with the current offering. This customer-centric approach allows businesses to identify high-impact improvement opportunities that can drive growth and build a competitive advantage. By understanding and addressing the disparity between importance and satisfaction, product teams can prioritize features and enhancements that truly resonate with their target audience. This technique rightfully earns its place among essential prioritization techniques for its ability to reveal hidden opportunities that traditional methods often miss.
Opportunity scoring utilizes a dual-metric evaluation system: importance and satisfaction. Customers are asked to rate both the importance of a specific feature or attribute and their level of satisfaction with the current solution’s performance on that attribute. The opportunity score is then calculated as: Importance + max(Importance - Satisfaction, 0). This formula ensures that features with high importance and low satisfaction receive the highest scores, highlighting the most pressing areas for improvement. Items where satisfaction meets or exceeds importance receive a score equal to their importance, signifying less urgent opportunities. This calculated score provides a clear and quantifiable metric for prioritizing features based on customer needs and perceptions, helping teams focus their efforts where they will have the greatest impact.
This prioritization technique is grounded in the gap analysis methodology, which systematically compares the current state to the desired state. By analyzing the gap between importance and satisfaction, product managers can pinpoint areas where improvements are most needed. This data-driven approach prevents assumption-based prioritization, ensuring that resources are allocated to initiatives that directly address customer pain points and enhance their experience. This is particularly crucial for project managers and team leads using platforms like Google Workspace, where understanding user needs and prioritizing feature enhancements can significantly impact productivity and user satisfaction. For small and medium-sized businesses, this technique offers a valuable framework for making strategic product decisions and optimizing their offerings to better serve their customer base.
Several successful examples demonstrate the power of opportunity scoring. Microsoft utilizes it to prioritize features in its Office suite, ensuring that updates address user needs and enhance productivity. Automotive companies leverage this method to understand which vehicle features require improvement, leading to more competitive and customer-centric designs. SaaS platforms like Salesforce rely on opportunity scoring to identify enhancement opportunities and prioritize their development roadmap. Even retail companies use this technique to optimize customer experience touchpoints, identifying and addressing friction points in the customer journey.
Actionable Tips for Implementing Opportunity Scoring:
- Use Large, Representative Customer Samples: To ensure accurate insights, gather feedback from a substantial and diverse group of customers that reflects your target market. For businesses operating within the Google Workspace ecosystem, this could involve surveying users across different departments and roles.
- Include Both Existing and Potential Customers: Understanding the needs of both groups provides a comprehensive view of market demands and potential growth areas.
- Validate Findings with Qualitative Research: While the quantitative data from surveys is valuable, supplementing it with qualitative research, like user interviews, can provide deeper context and uncover the "why" behind the ratings.
- Focus on High-Importance, Low-Satisfaction Areas First: These represent the biggest opportunities for improvement and should be prioritized in your development roadmap.
While opportunity scoring offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to be aware of its limitations:
- Requires Extensive Customer Research: Gathering robust data can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- May Not Account for Technical Feasibility: A highly desired feature might be technically challenging or prohibitively expensive to implement.
- Can Be Influenced by Survey Design: Poorly designed surveys can lead to biased or inaccurate results.
- Satisfaction Ratings May Be Contextual: Customer satisfaction can be influenced by external factors, making it essential to consider the broader context of the feedback.
Despite these potential drawbacks, the benefits of opportunity scoring often outweigh the challenges. By focusing on the gap between importance and satisfaction, businesses can make data-driven decisions that lead to meaningful product improvements, enhanced customer experiences, and a stronger competitive position. This is particularly relevant for sales teams and representatives using CRM systems within Google Workspace, as understanding customer needs and pain points is crucial for effective sales strategies and customer relationship management. Even individual professionals and freelancers can benefit from this technique to prioritize tasks and projects based on their importance and current level of progress, leading to increased efficiency and productivity. This method, popularized by Tony Ulwick, founder of Strategyn, and practitioners of the Jobs-to-be-Done methodology, provides a valuable framework for prioritizing efforts and achieving optimal results.
Prioritization Techniques: Side-by-Side Comparison
| Technique | Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Resource Requirements ⚡ | Expected Outcomes 📊 | Ideal Use Cases 💡 | Key Advantages ⭐ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eisenhower Matrix | Low - simple quadrant classification | Low - minimal tools needed | Prioritized tasks by urgency & importance | Personal productivity, strategic planning, executive decisions | Easy to use; promotes strategic focus; good delegation tool |
| MoSCoW Method | Medium - requires stakeholder facilitation | Medium - time and collaboration | Clear priority categorization of tasks | Project management, product development, requirements gathering | Strong stakeholder alignment; prevents scope creep |
| RICE Scoring Model | High - requires data estimation and calculation | Medium-High - data collection and analysis | Objective, numerical prioritization | Product management, growth initiatives, feature prioritization | Reduces bias; data-driven; multi-factor evaluation |
| Kano Model | Medium - requires customer survey design | High - extensive customer research | Customer satisfaction-based feature prioritization | Product development, customer experience, innovation | Customer-centric; identifies delighters and basics |
| Value vs. Effort Matrix | Low - visual plotting on two factors | Low - team input and workshops | Balanced initiatives by value and effort | Strategic planning, resource allocation, team prioritization | Intuitive visual tool; highlights quick wins and risks |
| Weighted Scoring Model | High - multi-criteria setup and scoring | High - stakeholder involvement | Quantitative, multi-factor decision making | Vendor selection, investment decisions, complex strategies | Handles complexity; transparent; accommodates diverse views |
| Story Mapping | Medium - requires mapping user stories | Medium - team workshops | User journey aligned feature prioritization | Product development, UX design, agile release planning | Maintains user focus; improves release planning; cross-team |
| Opportunity Scoring | Medium-High - customer surveys and gap analysis | High - significant customer research | Identifies high-impact improvement areas | Product improvement, customer experience, market research | Reveals hidden opportunities; customer-driven prioritization |
Ready to Prioritize Like a Pro?
This article explored eight powerful prioritization techniques, from the classic Eisenhower Matrix and MoSCoW Method to the more nuanced RICE scoring and Kano models. We also examined practical approaches like the Value vs. Effort Matrix, Weighted Scoring Model, Story Mapping, and Opportunity Scoring. Mastering these prioritization techniques is crucial for anyone managing projects, leading teams, or simply striving to enhance individual productivity. By understanding how to discern between urgent and important tasks, you gain the ability to strategically allocate your time and energy, leading to increased efficiency and better outcomes.
The key takeaway is that effective prioritization isn't about doing everything, but about doing the right things first. Whether you're a project manager juggling multiple deadlines, a sales representative managing leads, or a freelancer balancing various clients, consistent application of these prioritization techniques will drastically reduce overwhelm and empower you to achieve your most important goals.
Start small, experiment with different methods, and find what works best for you. Integrating these strategies into your workflow, combined with the right tools, can significantly impact your productivity and success. Supercharge your prioritization efforts with Tooling Studio's Kanban Tasks, designed to help you visualize and manage your prioritized tasks within Google Workspace. Visit Tooling Studio today to explore how it can streamline your workflow and help you achieve your goals faster.